Diagnostic Laparoscopy:


What is diagnostic laparoscopy?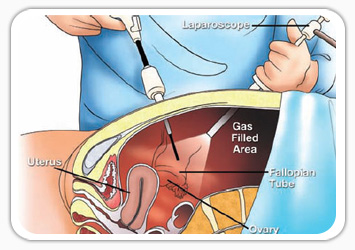
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a surgical procedure doctors use to view a woman's reproductive organs. A laparoscope, a thin viewing tube similar to a telescope, is passed through a small incision (cut) in the abdomen. Using the laparoscope, the doctor can look directly at the outside of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and nearby organs.
Laparoscopy is often recommended when other diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound and X-ray, cannot confirm the cause of a condition.
Your doctor might use laparoscopy to:
How is the procedure performed?
The procedure is performed while you are lying down in a slightly tilted position, with your head lower than your feet. You will be given a general anesthetic to relax your muscles and prevent pain during surgery.
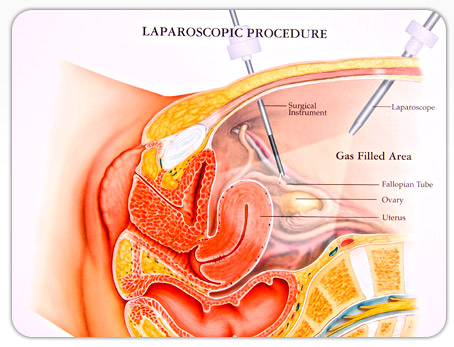 Next, a small incision is made near the navel. The laparoscope is inserted through this incision, and the abdomen is inflated to make the organs easier to view. The laparoscope might also be equipped with surgical devices for taking tissue samples or removing scar tissue.
Next, a small incision is made near the navel. The laparoscope is inserted through this incision, and the abdomen is inflated to make the organs easier to view. The laparoscope might also be equipped with surgical devices for taking tissue samples or removing scar tissue.
A second incision might also be made at the pubic hairline. This incision provides an additional opening for instruments needed for completing minor surgical procedures.
After surgery, patients generally stay in a recovery room for about one hour. Patients are then taken to an outpatient surgery unit for continued observation. You will be discharged after you receive instructions for your home recovery. In most cases, patients can leave the hospital about four hours after laparoscopy. Rarely a patient will need to stay overnight to aid recovery.
Patients are asked to return to their doctors for follow-up checkups within two to eight weeks. Please confirm your follow-up appointment before leaving the hospital.
Is laparoscopy safe?
Yes. Diagnostic laparoscopy is very safe. About three out of every 1,000 women who have laparoscopy have complications. Possible complications include injury to nearby organs, bleeding, or a problem related to the anesthesia. Discuss any concerns you have with your doctor.
Preparing for laparoscopy
Please follow these guidelines before coming to the hospital for your laparoscopy:
Recovering at home
Discomforts
Vaginal bleeding and menstruation
Vaginal bleeding up to one month after surgery is normal. Many women do not have their next normal menstrual cycle for four to six weeks after surgery. When your normal cycle returns, you might notice heavier bleeding and more discomfort than usual.
Wait two to three menstrual cycles before determining if laparoscopy has helped to relieve your condition.
Sexual activity
You can resume sexual activity one week after surgery. However, pregnancy can still occur during recovery. If you wish to prevent pregnancy, use a contraceptive.